To achieve net zero, the future of the transport, energy, consumer goods and many other sectors will eventually rely heavily on electrification. Advances in power electronics, machines, and drives (PEMD), battery technology, the development of innovative manufacturing processes, and building an appropriately trained workforce will be crucial to delivering the solutions.
Mike Capaldi, Dean of Business and Innovation, looks at the challenges and opportunities facing the battery industry in the UK, and introduces the University’s plan to create EPIC – the Electrification Process Innovation Centre – to meet the needs of the green industrial revolution.
The government’s commitment to phasing out all new purely petrol or diesel cars and vans by 2030 is presenting a huge challenge for the automotive industry.
To meet this target, the UK needs at least 90GWh battery manufacturing capacity by 2030. Currently only 14GWh capacity is in operation or construction. It is impossible to overstate the scale of the risk: in the UK more than 182,000 people are employed in vehicle manufacture, and some 780,000 in total across the wider automotive industry. This accounts for 10% of total UK exports with more than 150 countries importing UK produced vehicles, generating £77 billion of trade.

The North East of England is fast becoming established as an international leader in the electrification technologies that will be a major contributor to achieving net zero.
In response to the growing electrification challenge in the UK and globally, Newcastle University is leading the creation of an Electrification Process Innovation Centre (EPIC) to address the specific skills and capability challenges that industry is currently wrestling with.
So, what is EPIC?
EPIC is a Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV). EPIC brings together existing research and skills training organisations with industry to address the challenges that industry is currently faced with.
It is a collection of engineers, technicians and academics with core skills and technical knowledge in:
- Power electronics machines and drives (PEMD) and battery technology
- Manufacturing
- Process development
- Data
- Business
- Skills
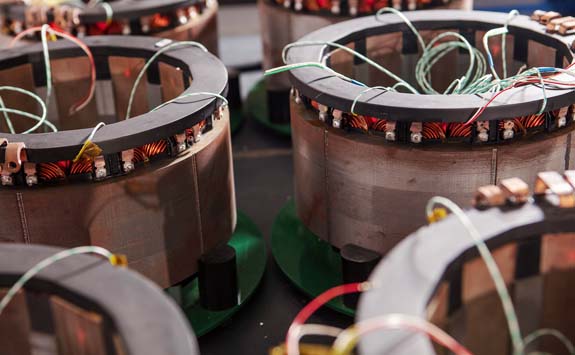
It will provide industry with a ‘one-stop shop’ for the capability required to grow their business, educate their workforce, and deliver manufacturing processing utilising the underpinning technologies required to deliver net zero.
EPIC will support the establishment and growth of an appropriately skilled workforce, positioning the North East as the epicentre for electrification process R&D, to drive inward investment and accelerate job growth.
Why is Newcastle University establishing EPIC?
Our vision for EPIC is that it will be the place where the manufacturing processes and skills for electrification will be pioneered. We will develop manufacturing processes and the skilled people needed to deliver them, at all levels, better equipping the world to accelerate the journey towards zero emissions.
EPIC will be a leading provider of industrially relevant skills-based education for electrification and the University’s vehicle for the delivery of degree apprenticeships and CPD in electrification.
Skills provision is crucial to the North East’s potential to be the epicentre of the UK’s future green economy. We have created the Institute of Electrification and Sustainable Advanced Manufacturing (IESAM), a partnership between the region’s universities and further education colleges and the North East Institute of Technology, funded by Innovate UK. IESAM provides a common curriculum for electrification skills aimed at students, apprentices, schoolteachers and college lecturers. IESAM is the first of its kind to address industry needs by developing a flexible, high-quality PEMD training pipeline in the North East.
Ultimately, EPIC will grow and enhance the University’s reputation as an international leader in electrification and lever this reputation to accelerate growth in activity and income across the whole research-innovation, education-skills pipeline.
-1.jpg?length=582&name=Stephenson_Building_Dusk_View%20(featured%20image)-1.jpg)
The North East’s Electrification Capabilities
The North East is fast becoming established as an international leader in electrification technologies. Underpinning this potential is a whole ecosystem that is poised and ready to connect and work with the rest of the UK:
2. The UK’s first two battery gigafactories, Envision and Recharge Industries (formerly Britishvolt) are located here;
3. The Faraday Institution has opened its first UK regional office in Newcastle University (FINE), which along with the North East Battery Alliance is supporting the rapidly growing battery sector;
4. The national Driving the Electric Revolution Industrialisation Centre (DER-IC) programme, led by Newcastle University, is establishing a power electronics, machines and drives (PEMD) component supply chain for the UK’s growing electrification industry. The DER Industrialisation Centre NE, based in Sunderland, is focussed on developing solutions for electrifying the automotive, rail and marine sectors;
5. We have created the Institute of Electrification and Sustainable Advanced Manufacturing (IESAM), a partnership between the region’s universities and further education colleges and the North East Institute of Technology, funded by Innovate UK. IESAM provides a common curriculum for electrification skills aimed at students, apprentices, schoolteachers and college lecturers. It is the first centre of its kind to address industry needs by developing a flexible, high-quality PEMD training pipeline in the North East;
7. The UK’s largest offshore wind farm is being developed at Dogger Bank, off the North East coast, supported by the UK’s leading technology and research centre for offshore renewable energy, OREC, based in Blyth, South Northumberland. This is driving a new off-shore ecosystem on the NE coast with inward investment from major international companies such as Equinor and JDR Cables.
We need to harness this existing potential, not only to maximise these opportunities but also to ensure the future sustainability of the UK’s transport, energy, consumer goods and other manufacturing sectors by putting in place a plan to train and upskill the workforce of the future.
Quotes from partners
"EPIC aligns very strongly with CPI’s strategy on Net Zero in particular sustainable materials, and we see this particular programme as a substantial, long term, strategic partnership opportunity within our network. Given our core interest in Energy Materials, we are excited to participate in and support EPIC both nationally and through the Faraday Institute North East."
- Centre for Process Innovation
- North East Automotive Alliance
"We believe that EPIC has the potential to transform the battery industry, and we are eager to be part of this effort."
- The Faraday Institution

.jpg?length=1920&name=News%20(Desktop%201800x1213).jpg)